Worried about Why blockchain is the future? This post will show you why blockchain is the future of the internet. In recent years, actually, there has been a lot of discussion and conjecture about the internet’s future. The proliferation of social media and the emergence of virtual worlds and immersive experiences have both contributed to the internet’s ubiquity as a medium for communication and business. The growth of blockchain signals a significant change coming to the internet.
Blockchain is the Future? Everything You Need To Know
The internet has seen other changes before. The internet has undergone two significant evolutions since it first became widely used, and a third is soon to follow.
These changes have affected society as a whole, altering how we live, work, and interact with one another. They have transformed how we use the internet and what we use it for.
Web 1.0: The static Internet
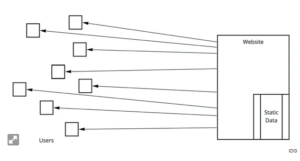
The age of the website was the first version of the public internet. Every business required a website, which often featured static data and content that the website’s owner deemed significant.
The corporate website contained details about the business, primarily marketing materials. Websites for news and information also had a wealth of data. However, each of these websites only provided a one-way information push to the user.
This was comparable to how information was distributed to the general public through the traditional media of the day (newspapers, magazines, radio, and television). Every business, whether it was a corporate brand like McDonald’s or an established news organisation like NBC or CNN, quickly had a website that disseminated information to the general public.
This internet is demonstrated in Figure 1. A website was a thing that was made and owned by a business. The majority of the data was static, and the corporation was in charge of and managed the data. Information was disseminated to website visitors in a single route. Given the one-way nature of the information in this architecture, data personalisation was severely constrained. This article shows you why blockchain is the future of the internet.
Users could choose and filter the material they wanted to read, but they often had little control over what was transmitted in that information. Users had almost no effect over one another.
Computer users would often only share information with their local networks of friends or message board communities. These represented extremely narrow and concentrated audiences.
Web 2.0: The web application
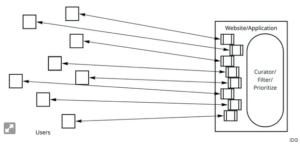
The web application era began with the second generation of the public internet, which is the one you’re currently using. Here, businesses concentrate on giving people a forum to communicate with one another.
Personal blogging became popular thanks to Web 2.0, and this tendency later spread to the social media environment we see today. The democratisation of data was pioneered by businesses like Twitter and Facebook. They developed tools that let anyone post almost anything on any subject and share it with a sizable audience.
As shown in Figure 2, our current internet architecture, online applications and social networks run by businesses like Facebook offer users a platform to enter data and share it either privately with “friends” or publicly with anybody who might be interested.
With the help of modern web applications, users can speak with strangers on the other side of the planet. The use of the internet significantly increased when smartphones were widely available.
Now everyone could have constant access to the internet. Anybody they wanted to talk to could do so whenever they wished and from any location. The internet blew up.
While users discovered they could speak with people all over the world, the businesses that owned these applications discovered they could gather enormous amounts of data about users and their preferences.
The internet titans turned to this data as a priceless source of knowledge and a significant source of income.
The founders of firms like Facebook became some of the richest people in the world as they expanded into multibillion dollar megacorporations. Then, these businesses learned that curating was something else they could do.
They may utilise data they obtained about people’s preferences to tailor information sharing to people’s interests rather than dispersing information from one user to another at random. Web application businesses had enormous power to control the information that individuals around the world received when the “social algorithm” was created.
These firms are now incredibly powerful—many people think they are too powerful—thanks to their control over information.
Web 3.0: Authoritative data
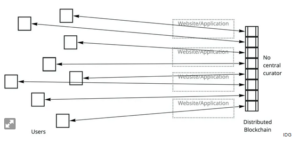
Right now, the third generation of the public internet is just around the corner. In this third generation, web applications are no longer responsible for storing and maintaining data. Data and information are instead kept in the structure of the internet itself.
In Web 3.0, data is made accessible to any programme that requires it and has permission to utilise it. The data is no longer under the control of a web platform provider like Facebook or owned by an application. Web apps actually have a very minor impact on how information is managed.
There isn’t a super-powerful social media firm that can decide what information users are permitted to see because no single programme can fulfil the function of an information curator. End users manage and control their data and information alone, using and managing it independently of any one firm.
Although none of the online applications control or manage the information, they are consumers of it. Web applications are therefore no longer as important as the data itself.
Instead, data and information are kept on a distributed blockchain that is not controlled by a single business. Since every internet corporation has access to every piece of information in the blockchain equally, no single entity can control it (company or government).
Figure 3 by IDG. Distributed, reliable data in Web 3.0. The objective is to make it possible to share unfiltered, uncurated, authoritative information that is not influenced unfairly by web applications.
Instead of being owned and controlled by online applications and their developers, the data is actually owned and managed by the users. As a result of data being sourced, cited, and unfiltered, the internet will become more reliable and trustworthy.
Web 3.0 is expected to establish a more decentralised power structure on the internet than Web 2.0’s web platform providers ever could. The Value of Blockchain
A single piece of technology—blockchain—enables this revolution that will give rise to the third generation of the internet. This distributed, data-first, authoritative internet is built around a blockchain.
Why is blockchain technology such a key component of this revolution?
The following characteristics of blockchain will make this shift possible:
In a blockchain, ownership is distributed. The ownership of the data on a blockchain is not centralised. A blockchain is accessible to everyone and anyone can read from it. A blockchain’s distribution is open to everyone.
- Because a blockchain stores data that is immutable, irrevocable, and cryptographically signed, it can be proven to be true and authoritative (or provably inauthentic and unauthoratative).
All data can be verified as to its source and veracity, and everyone knows who is its owner and creator. This raises confidence in the accuracy of the data.
- The data on a blockchain cannot be curated, moderated, prioritised, or filtered by a single company.
No one can control how the data is used by users because there is no single owner of the data. This indicates that there aren’t any data power brokers controlling and managing the information that is shared, like social media firms.
In other words, by making all transactions visible and data verifiable, blockchain promotes trust in data and its source. As there’s no single owner of the internet’s communications backbone, blockchain is akin to the IP transportation infrastructure of the internet.
The backbone is supported by organisations including AT&T, Verizon, Deutsche Telekom, and NTT Communications.
However, no single owner is able to entirely isolate, filter, or prevent internet traffic. Even strong nations like China and Russia, which seek to keep certain areas of the internet off-limits to their population, find the task to be an ongoing fight.
All filtering is useless since all it takes to establish a new communications line is a new, unfiltered provider.
What the internet backbone has done for information dissemination, blockchain will do for internet data. It will produce a reliable, uncensorable, and accessible global data and data repository. This quality will actually guide the development of the third generation of the internet. And for this reason, the blockchain is essential to the internet’s future.
What Blockchain Means for Enterprises
The most obvious piece of advise is to educate yourself on blockchain as much as possible. Do not mix up blockchain with Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. Blockchain is used by Bitcoin, although Bitcoin is not a blockchain. The benefits of blockchain extend far beyond its usage in cryptocurrencies at first.
Next, understand that blockchain is more than simply a technology; it also represents a fundamentally novel approach to thinking about data that will usher in a new era of the internet. It is equally essential to data as the internet’s backbone is to the transmission of information.
Keep blockchain in mind as you begin to consider the architectures of your future application. As the public cloud, microservice architectures, and the devops are to the current generation of internet apps, blockchain will be crucial to the following one. Ensure that all of your application architecture strategies for present and future applications take blockchain into account.

